1. 关联概述
Active Record 关联允许你定义模型之间的关系。关联以特殊的宏式调用实现,可以轻松地告诉 Rails 你的模型如何相互关联,这有助于你更有效地管理数据,并使常见操作更简单易读。
宏式调用是一种在运行时生成或修改其他方法的方法,允许简洁明了地声明功能,例如在 Rails 中定义模型关联。例如,has_many :comments。
当你设置关联时,Rails 会帮助定义和管理两个模型实例之间的主键和外键关系,而数据库则确保你的数据保持一致和正确链接。
这使得跟踪哪些记录相关变得容易。它还为你的模型添加了有用的方法,以便你可以更轻松地处理相关数据。
考虑一个简单的 Rails 应用程序,其中包含作者和书籍的模型。
1.1. 无关联
没有关联,为该作者创建和删除书籍将需要一个繁琐的手动过程。以下是它的样子
class CreateAuthors < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :authors do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :books do |t|
t.references :author
t.datetime :published_at
t.timestamps
end
end
end
class Author < ApplicationRecord
end
class Book < ApplicationRecord
end
要为现有作者添加新书,你需要在创建书籍时提供 author_id 值。
@book = Book.create(author_id: @author.id, published_at: Time.now)
要删除作者并确保其所有书籍也都被删除,你需要检索作者的所有 books,遍历每本 book 以销毁它,然后销毁作者。
@books = Book.where(author_id: @author.id)
@books.each do |book|
book.destroy
end
@author.destroy
1.2. 使用关联
然而,通过关联,我们可以通过明确告知 Rails 两个模型之间的关系来简化这些操作以及其他操作。以下是使用关联设置作者和书籍的修订代码
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, dependent: :destroy
end
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author
end
通过此更改,为特定作者创建新书变得更简单
@book = @author.books.create(published_at: Time.now)
删除作者及其所有书籍变得容易得多
@author.destroy
当你在 Rails 中设置关联时,你仍然需要创建迁移以确保数据库已正确配置以处理关联。此迁移将需要将必要的外键列添加到数据库表中。
例如,如果你在 Book 模型中设置 belongs_to :author 关联,你将创建一个迁移以将 author_id 列添加到 books 表中
rails generate migration AddAuthorToBooks author:references
此迁移将添加 author_id 列并在数据库中设置外键关系,确保你的模型和数据库保持同步。
要了解不同类型的关联,你可以阅读本指南的下一节。之后,你会发现一些使用关联的提示和技巧。最后,还有 Rails 中关联的方法和选项的完整参考。
2. 关联类型
Rails 支持六种关联类型,每种都有特定的用例。
以下是所有支持的类型列表,其中包含指向其 API 文档的链接,以获取有关如何使用它们、它们的方法参数等的更详细信息。
在本指南的其余部分,你将学习如何声明和使用各种形式的关联。首先,让我们快速了解每种关联类型适用的情况。
2.1. belongs_to
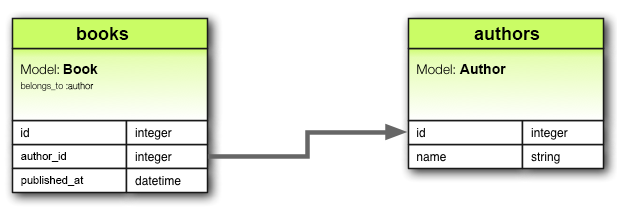
belongs_to 关联设置了与另一个模型的关系,使得声明模型的每个实例“属于”另一个模型的一个实例。例如,如果你的应用程序包含作者和书籍,并且每本书只能分配给一个作者,你可以这样声明书籍模型
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author
end
belongs_to 关联必须使用单数形式。如果你使用复数形式,例如在 Book 模型中使用 belongs_to :authors,并尝试使用 Book.create(authors: @author) 创建一本书,Rails 将给你一个“uninitialized constant Book::Authors”错误。这是因为 Rails 会自动从关联名称推断类名。如果关联名称是 :authors,Rails 将查找名为 Authors 的类而不是 Author。
相应的迁移可能看起来像这样
class CreateBooks < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :authors do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :books do |t|
t.belongs_to :author
t.datetime :published_at
t.timestamps
end
end
end
在数据库术语中,belongs_to 关联表示此模型的表包含一个列,该列表示对另一个表的引用。这可以用于设置一对一或一对多关系,具体取决于设置。如果另一个类的表在一对一关系中包含引用,那么你应该改用 has_one。
单独使用时,belongs_to 产生单向的一对一关系。因此,上述示例中的每本书都“知道”其作者,但作者不知道他们的书籍。要设置双向关联,请在另一个模型(在此示例中为 Author 模型)上结合使用 belongs_to 和 has_one 或 has_many。
默认情况下,belongs_to 验证关联记录的存在以保证引用一致性。
如果在模型中将 optional 设置为 true,则 belongs_to 不保证引用一致性。这意味着一个表中的外键可能无法可靠地指向引用表中有效的 PRIMARY KEY。
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, optional: true
end
因此,根据用例,你可能还需要在引用列上添加数据库级外键约束,如下所示
create_table :books do |t|
t.belongs_to :author, foreign_key: true
# ...
end
这确保了即使 optional: true 允许 author_id 为 NULL,当它不为 NULL 时,它仍然必须引用 authors 表中的有效记录。
2.1.1. belongs_to 添加的方法
当你声明 belongs_to 关联时,声明类会自动获得与该关联相关的众多方法。其中一些是
association=(associate)build_association(attributes = {})create_association(attributes = {})create_association!(attributes = {})reload_associationreset_associationassociation_changed?association_previously_changed?
我们将讨论一些常用方法,但你可以在ActiveRecord Associations API中找到详尽列表。
在上述所有方法中,association 被替换为作为 belongs_to 的第一个参数传递的符号。例如,给定声明
# app/models/book.rb
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author
end
# app/models/author.rb
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
validates :name, presence: true
end
Book 模型的一个实例将具有以下方法
authorauthor=build_authorcreate_authorcreate_author!reload_authorreset_authorauthor_changed?author_previously_changed?
初始化新的 has_one 或 belongs_to 关联时,你必须使用 build_ 前缀来构建关联,而不是用于 has_many 或 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联的 association.build 方法。要创建一个,请使用 create_ 前缀。
2.1.1.1. 检索关联
association 方法返回关联对象(如果有)。如果没有找到关联对象,它返回 nil。
@author = @book.author
如果关联对象已从数据库中为此对象检索,则将返回缓存版本。要覆盖此行为(并强制从数据库读取),请在父对象上调用 #reload_association。
@author = @book.reload_author
要卸载关联对象的缓存版本(导致下次访问(如果有)从数据库中查询它),请在父对象上调用 #reset_association。
@book.reset_author
2.1.1.2. 分配关联
association= 方法将关联对象分配给此对象。在幕后,这意味着从关联对象中提取主键并将此对象的外键设置为相同的值。
@book.author = @author
build_association 方法返回关联类型的新对象。此对象将从传递的属性实例化,并通过此对象的外键设置链接,但关联对象将尚未保存。
@author = @book.build_author(author_number: 123,
author_name: "John Doe")
create_association 方法更进一步,一旦通过关联模型上指定的所有验证,它还会保存关联对象。
@author = @book.create_author(author_number: 123,
author_name: "John Doe")
最后,create_association! 执行相同操作,但如果记录无效则引发 ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid。
# This will raise ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid because the name is blank
begin
@book.create_author!(author_number: 123, name: "")
rescue ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid => e
puts e.message
end
irb> raise_validation_error: Validation failed: Name can't be blank (ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid)
2.1.1.3. 检查关联更改
如果已分配新的关联对象并且外键将在下次保存时更新,则 association_changed? 方法返回 true。
如果上次保存更新了关联以引用新的关联对象,则 association_previously_changed? 方法返回 true。
@book.author # => #<Author author_number: 123, author_name: "John Doe">
@book.author_changed? # => false
@book.author_previously_changed? # => false
@book.author = Author.second # => #<Author author_number: 456, author_name: "Jane Smith">
@book.author_changed? # => true
@book.save!
@book.author_changed? # => false
@book.author_previously_changed? # => true
不要混淆 model.association_changed? 和 model.association.changed?。前者检查关联是否已替换为新记录,而后者跟踪关联属性的更改。
2.1.1.4. 检查现有关联
你可以通过使用 association.nil? 方法查看是否存在任何关联对象
if @book.author.nil?
@msg = "No author found for this book"
end
2.1.1.5. 关联对象的保存行为
将对象分配给 belongs_to 关联不会自动保存当前对象或关联对象。但是,当你保存当前对象时,关联也会保存。
2.2. has_one
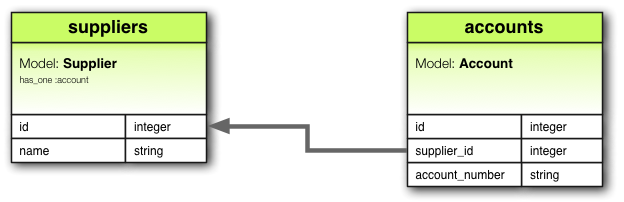
has_one 关联表示另一个模型对此模型有一个引用。该模型可以通过此关联获取。
例如,如果你的应用程序中的每个供应商只有一个帐户,你可以这样声明供应商模型
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account
end
与 belongs_to 的主要区别在于链接列(在本例中为 supplier_id)位于另一个表中,而不是声明 has_one 的表中。
相应的迁移可能看起来像这样
class CreateSuppliers < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :suppliers do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :accounts do |t|
t.belongs_to :supplier
t.string :account_number
t.timestamps
end
end
end
has_one 关联创建与另一个模型的一对一匹配。在数据库术语中,此关联表示另一个类包含外键。如果此类包含外键,那么你应该改用 belongs_to。
根据用例,你可能还需要在 accounts 表的 supplier 列上创建唯一索引和/或外键约束。唯一索引确保每个供应商只与一个帐户关联,并允许你以高效的方式查询,而外键约束确保 accounts 表中的 supplier_id 引用 suppliers 表中的有效 supplier。这会在数据库级别强制执行关联。
create_table :accounts do |t|
t.belongs_to :supplier, index: { unique: true }, foreign_key: true
# ...
end
当与另一个模型上的 belongs_to 结合使用时,此关系可以是双向的。
2.2.1. has_one 添加的方法
当你声明 has_one 关联时,声明类会自动获得与该关联相关的众多方法。其中一些是
associationassociation=(associate)build_association(attributes = {})create_association(attributes = {})create_association!(attributes = {})reload_associationreset_association
我们将讨论一些常用方法,但你可以在ActiveRecord Associations API中找到详尽列表。
与belongs_to 引用一样,在所有这些方法中,association 被替换为作为 has_one 的第一个参数传递的符号。例如,给定声明
# app/models/supplier.rb
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account
end
# app/models/account.rb
class Account < ApplicationRecord
validates :terms, presence: true
belongs_to :supplier
end
Supplier 模型的每个实例将具有这些方法
accountaccount=build_accountcreate_accountcreate_account!reload_accountreset_account
初始化新的 has_one 或 belongs_to 关联时,你必须使用 build_ 前缀来构建关联,而不是用于 has_many 或 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联的 association.build 方法。要创建一个,请使用 create_ 前缀。
2.2.1.1. 检索关联
association 方法返回关联对象(如果有)。如果没有找到关联对象,它返回 nil。
@account = @supplier.account
如果关联对象已从数据库中为此对象检索,则将返回缓存版本。要覆盖此行为(并强制从数据库读取),请在父对象上调用 #reload_association。
@account = @supplier.reload_account
要卸载关联对象的缓存版本(强制下次访问(如果有)从数据库中查询它),请在父对象上调用 #reset_association。
@supplier.reset_account
2.2.1.2. 分配关联
association= 方法将关联对象分配给此对象。在幕后,这意味着从此对象中提取主键并将关联对象的外键设置为相同的值。
@supplier.account = @account
build_association 方法返回关联类型的新对象。此对象将从传递的属性实例化,并通过此对象的外键设置链接,但关联对象将尚未保存。
@account = @supplier.build_account(terms: "Net 30")
create_association 方法更进一步,一旦通过关联模型上指定的所有验证,它还会保存关联对象。
@account = @supplier.create_account(terms: "Net 30")
最后,create_association! 执行与上述 create_association 相同操作,但如果记录无效则引发 ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid。
# This will raise ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid because the terms is blank
begin
@supplier.create_account!(terms: "")
rescue ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid => e
puts e.message
end
irb> raise_validation_error: Validation failed: Terms can't be blank (ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid)
2.2.1.3. 检查现有关联
你可以通过使用 association.nil? 方法查看是否存在任何关联对象
if @supplier.account.nil?
@msg = "No account found for this supplier"
end
2.2.1.4. 关联对象的保存行为
当你将对象分配给 has_one 关联时,该对象会自动保存以更新其外键。此外,任何被替换的对象也会自动保存,因为其外键也会更改。
如果这些保存中的任何一个因验证错误而失败,则赋值语句返回 false,并且赋值本身被取消。
如果父对象(声明 has_one 关联的对象)未保存(即 new_record? 返回 true),则子对象不会立即保存。它们将在父对象保存时自动保存。
如果你想将对象分配给 has_one 关联而不保存对象,请使用 build_association 方法。此方法创建关联对象的新未保存实例,允许你在决定保存之前使用它。
当你想要控制模型关联对象的保存行为时,请使用 autosave: false。此设置阻止关联对象在父对象保存时自动保存。相反,当你需要处理未保存的关联对象并延迟其持久化直到你准备好时,请使用 build_association。
2.3. has_many
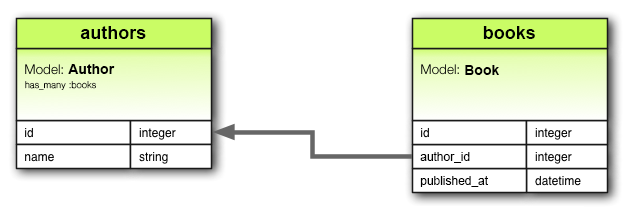
has_many 关联类似于 has_one,但表示与另一个模型的一对多关系。你经常会在 belongs_to 关联的“另一端”找到此关联。此关联表示模型的每个实例具有零个或多个另一个模型的实例。例如,在包含作者和书籍的应用程序中,作者模型可以这样声明
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
end
has_many 在模型之间建立一对多关系,允许声明模型的每个实例 (Author) 拥有关联模型 (Book) 的多个实例。
与 has_one 和 belongs_to 关联不同,声明 has_many 关联时,另一个模型的名称是复数形式。
相应的迁移可能看起来像这样
class CreateAuthors < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :authors do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :books do |t|
t.belongs_to :author
t.datetime :published_at
t.timestamps
end
end
end
has_many 关联创建与另一个模型的一对多关系。在数据库术语中,此关联表示另一个类将具有引用此类实例的外键。
在此迁移中,创建 authors 表时带有一个 name 列,用于存储作者的姓名。还创建 books 表,并包含 belongs_to :author 关联。此关联在 books 和 authors 表之间建立外键关系。具体来说,books 表中的 author_id 列充当外键,引用 authors 表中的 id 列。通过在 books 表中包含此 belongs_to :author 关联,我们确保每本书都与单个作者关联,从而允许从 Author 模型进行 has_many 关联。此设置允许每个作者拥有多个关联书籍。
根据用例,通常最好为 books 表的 author 列创建非唯一索引和可选的外键约束。在 author_id 列上添加索引可以提高检索与特定作者关联的书籍时的查询性能。
如果你希望在数据库级别强制执行参照完整性,请在上面的 reference 列声明中添加foreign_key: true 选项。这将确保 books 表中的 author_id 必须对应 authors 表中的有效 id,
create_table :books do |t|
t.belongs_to :author, index: true, foreign_key: true
# ...
end
当与另一个模型上的 belongs_to 结合使用时,此关系可以是双向的。
2.3.1. has_many 添加的方法
当你声明 has_many 关联时,声明类会自动获得与该关联相关的众多方法。其中一些是
collectioncollection<<(object, ...)collection.delete(object, ...)collection.destroy(object, ...)collection=(objects)collection_singular_idscollection_singular_ids=(ids)collection.clearcollection.empty?collection.sizecollection.find(...)collection.where(...)collection.exists?(...)collection.build(attributes = {})collection.create(attributes = {})collection.create!(attributes = {})collection.reload
我们将讨论一些常用方法,但你可以在ActiveRecord Associations API中找到详尽列表。
在所有这些方法中,collection 被替换为作为 has_many 的第一个参数传递的符号,collection_singular 被替换为该符号的单数版本。例如,给定声明
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
end
Author 模型的一个实例可以具有以下方法
books
books<<(object, ...)
books.delete(object, ...)
books.destroy(object, ...)
books=(objects)
book_ids
book_ids=(ids)
books.clear
books.empty?
books.size
books.find(...)
books.where(...)
books.exists?(...)
books.build(attributes = {}, ...)
books.create(attributes = {})
books.create!(attributes = {})
books.reload
2.3.1.1. 管理集合
collection 方法返回所有关联对象的 Relation。如果没有关联对象,它返回一个空的 Relation。
@books = @author.books
collection.delete 方法通过将其外键设置为 NULL 从集合中删除一个或多个对象。
@author.books.delete(@book1)
此外,如果对象与 dependent: :destroy 关联,它们将被销毁;如果与 dependent: :delete_all 关联,它们将被删除。
collection.destroy 方法通过对每个对象运行 destroy 从集合中删除一个或多个对象。
@author.books.destroy(@book1)
对象将始终从数据库中删除,忽略 :dependent 选项。
collection.clear 方法根据 dependent 选项指定的策略从集合中删除所有对象。如果未给定选项,它将遵循默认策略。has_many :through 关联的默认策略是 delete_all,has_many 关联的默认策略是将外键设置为 NULL。
@author.books.clear
如果对象与 dependent: :destroy 或 dependent: :destroy_async 关联,它们将被删除,就像 dependent: :delete_all 一样。
collection.reload 方法返回所有关联对象的 Relation,强制从数据库读取。如果没有关联对象,它返回一个空的 Relation。
@books = @author.books.reload
2.3.1.2. 分配集合
collection=(objects) 方法通过适当的添加和删除,使集合仅包含提供的对象。更改将持久化到数据库。
collection_singular_ids=(ids) 方法通过适当的添加和删除,使集合仅包含由提供的主键值标识的对象。更改将持久化到数据库。
2.3.1.3. 查询集合
collection_singular_ids 方法返回集合中对象的 id 数组。
@book_ids = @author.book_ids
collection.empty? 方法返回 true 如果集合不包含任何关联对象。
<% if @author.books.empty? %>
No Books Found
<% end %>
collection.size 方法返回集合中对象的数量。
@book_count = @author.books.size
collection.find 方法在集合的表中查找对象。
@available_book = @author.books.find(1)
collection.where 方法根据提供的条件在集合中查找对象,但对象是延迟加载的,这意味着只有在访问对象时才查询数据库。
@available_books = @author.books.where(available: true) # No query yet
@available_book = @available_books.first # Now the database will be queried
collection.exists? 方法检查集合的表中是否存在满足提供条件的对象。
2.3.1.4. 构建和创建关联对象
collection.build 方法返回一个或多个关联类型的新对象。对象将从传递的属性实例化,并通过其外键创建链接,但关联对象将尚未保存。
@book = @author.books.build(published_at: Time.now,
book_number: "A12345")
@books = @author.books.build([
{ published_at: Time.now, book_number: "A12346" },
{ published_at: Time.now, book_number: "A12347" }
])
collection.create 方法返回一个或多个关联类型的新对象。对象将从传递的属性实例化,并通过其外键创建链接,并且,一旦通过关联模型上指定的所有验证,关联对象将被保存。
@book = @author.books.create(published_at: Time.now,
book_number: "A12345")
@books = @author.books.create([
{ published_at: Time.now, book_number: "A12346" },
{ published_at: Time.now, book_number: "A12347" }
])
collection.create! 执行与 collection.create 相同操作,但如果记录无效则引发 ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid。
2.3.1.5. 对象何时保存?
当你将对象分配给 has_many 关联时,该对象会自动保存(以便更新其外键)。如果你在一个语句中分配多个对象,那么它们都将被保存。
如果这些保存中的任何一个因验证错误而失败,则赋值语句返回 false,并且赋值本身被取消。
如果父对象(声明 has_many 关联的对象)未保存(即 new_record? 返回 true),则子对象在添加时不会保存。关联的所有未保存成员将在父对象保存时自动保存。
如果你想将对象分配给 has_many 关联而不保存对象,请使用 collection.build 方法。
2.4. has_many :through
has_many :through 关联通常用于设置与另一个模型的多对多关系。此关联表示声明模型可以通过中间“连接”模型与另一个模型的零个或多个实例匹配。
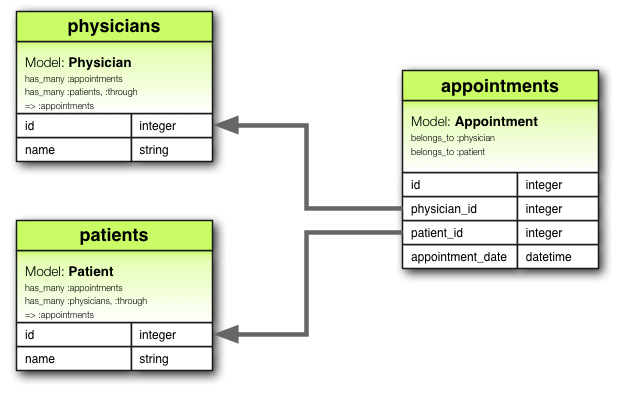
例如,考虑一个医疗实践,患者预约看医生。相关的关联声明可能如下所示
class Physician < ApplicationRecord
has_many :appointments
has_many :patients, through: :appointments
end
class Appointment < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :physician
belongs_to :patient
end
class Patient < ApplicationRecord
has_many :appointments
has_many :physicians, through: :appointments
end
has_many :through 在模型之间建立多对多关系,允许一个模型 (Physician) 的实例通过第三个“连接”模型 (Appointment) 与另一个模型 (Patient) 的多个实例关联。
我们将 Physician.appointments 和 Appointment.patient 分别称为 Physician.patients 的通过和源关联。
相应的迁移可能看起来像这样
class CreateAppointments < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :physicians do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :patients do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :appointments do |t|
t.belongs_to :physician
t.belongs_to :patient
t.datetime :appointment_date
t.timestamps
end
end
end
在此迁移中,physicians 和 patients 表是使用 name 列创建的。作为连接表的 appointments 表是使用 physician_id 和 patient_id 列创建的,从而在 physicians 和 patients 之间建立多对多关系。
通过关联可以是任何类型的关联,包括其他通过关联,但它不能是多态的。源关联可以是多态的,只要你提供源类型。
你还可以考虑在 has_many :through 关系中使用复合主键作为连接表,如下所示
class CreateAppointments < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
# ...
create_table :appointments, primary_key: [:physician_id, :patient_id] do |t|
t.belongs_to :physician
t.belongs_to :patient
t.datetime :appointment_date
t.timestamps
end
end
end
has_many :through 关联中的连接模型集合可以使用标准has_many 关联方法进行管理。例如,如果你将患者列表分配给医生,如下所示
physician.patients = patients
Rails 将自动为新列表中以前未与医生关联的任何患者创建新的连接模型。此外,如果以前与医生关联的任何患者未包含在新列表中,其连接记录将自动删除。这通过为你处理连接模型的创建和删除来简化多对多关系的管理。
连接模型的自动删除是直接的,不会触发销毁回调。你可以在Active Record 回调指南中阅读有关回调的更多信息。
has_many :through 关联对于通过嵌套 has_many 关联设置“快捷方式”也很有用。当你需要通过中间关联访问相关记录集合时,这尤其有利。
例如,如果一个文档有许多部分,并且每个部分有许多段落,你可能有时希望获得文档中所有段落的简单集合,而无需手动遍历每个部分。
你可以使用 has_many :through 关联进行设置,如下所示
class Document < ApplicationRecord
has_many :sections
has_many :paragraphs, through: :sections
end
class Section < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :document
has_many :paragraphs
end
class Paragraph < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :section
end
指定 through: :sections 后,Rails 现在将理解
@document.paragraphs
然而,如果你没有设置 has_many :through 关联,你将需要执行类似以下操作才能在文档中获取段落
paragraphs = []
@document.sections.each do |section|
paragraphs.concat(section.paragraphs)
end
2.5. has_one :through
has_one :through 关联通过中间模型设置与另一个模型的一对一关系。此关联表示声明模型可以通过第三个模型与另一个模型的一个实例匹配。
例如,如果每个供应商有一个帐户,并且每个帐户都与一个帐户历史记录关联,则供应商模型可能如下所示
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account
has_one :account_history, through: :account
end
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier
has_one :account_history
end
class AccountHistory < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :account
end
此设置允许 supplier 通过其 account 直接访问其 account_history。
我们将 Supplier.account 和 Account.account_history 分别称为 Supplier.account_history 的通过和源关联。
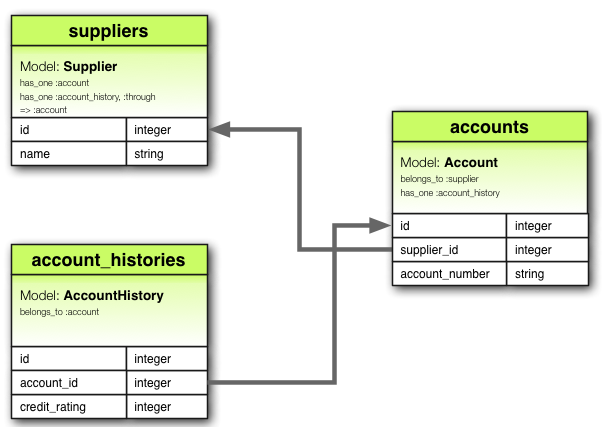
设置这些关联的相应迁移可能如下所示
class CreateAccountHistories < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :suppliers do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :accounts do |t|
t.belongs_to :supplier
t.string :account_number
t.timestamps
end
create_table :account_histories do |t|
t.belongs_to :account
t.integer :credit_rating
t.timestamps
end
end
end
通过关联必须是 has_one、has_one :through 或非多态的 belongs_to。也就是说,一个非多态的单数关联。另一方面,源关联可以是多态的,只要你提供源类型。
2.6. has_and_belongs_to_many
has_and_belongs_to_many 关联创建与另一个模型的直接多对多关系,没有中间模型。此关联表示声明模型的每个实例引用另一个模型的零个或多个实例。
例如,考虑一个具有 Assembly 和 Part 模型的应用程序,其中每个装配可以包含多个零件,每个零件可以在多个装配中使用。你可以按如下方式设置模型
class Assembly < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :parts
end
class Part < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies
end
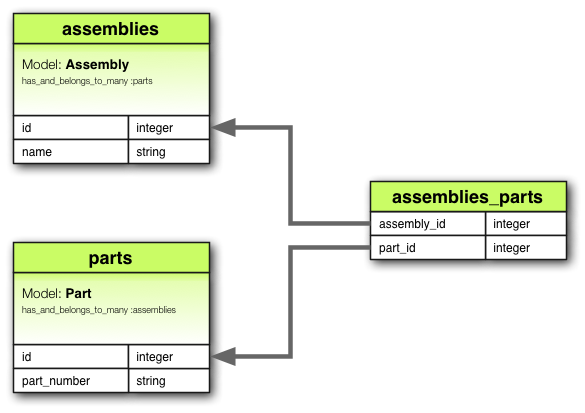
尽管 has_and_belongs_to_many 不需要中间模型,但它需要一个单独的表来建立所涉及的两个模型之间的多对多关系。这个中间表用于存储相关数据,映射两个模型实例之间的关联。该表不一定需要主键,因为其目的仅仅是管理关联记录之间的关系。相应的迁移可能如下所示
class CreateAssembliesAndParts < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :assemblies do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :parts do |t|
t.string :part_number
t.timestamps
end
# Create a join table to establish the many-to-many relationship between assemblies and parts.
# `id: false` indicates that the table does not need a primary key of its own
create_table :assemblies_parts, id: false do |t|
# creates foreign keys linking the join table to the `assemblies` and `parts` tables
t.belongs_to :assembly
t.belongs_to :part
end
end
end
has_and_belongs_to_many 关联创建与另一个模型的多对多关系。在数据库术语中,这通过一个中间连接表关联两个类,该连接表包含引用每个类的外键。
如果 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联的连接表除了两个外键之外还有其他列,则这些列将作为属性添加到通过该关联检索的记录中。返回的具有额外属性的记录将始终是只读的,因为 Rails 无法保存对这些属性的更改。
在 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联的连接表中使用额外属性已被弃用。如果你需要在连接两个模型的多对多关系表中进行这种复杂的行为,你应该使用 has_many :through 关联而不是 has_and_belongs_to_many。
2.6.1. has_and_belongs_to_many 添加的方法
当你声明 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联时,声明类会自动获得与该关联相关的众多方法。其中一些是
collectioncollection<<(object, ...)collection.delete(object, ...)collection.destroy(object, ...)collection=(objects)collection_singular_idscollection_singular_ids=(ids)collection.clearcollection.empty?collection.sizecollection.find(...)collection.where(...)collection.exists?(...)collection.build(attributes = {})collection.create(attributes = {})collection.create!(attributes = {})collection.reload
我们将讨论一些常用方法,但你可以在ActiveRecord Associations API中找到详尽列表。
在所有这些方法中,collection 被替换为作为 has_and_belongs_to_many 的第一个参数传递的符号,collection_singular 被替换为该符号的单数版本。例如,给定声明
class Part < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies
end
Part 模型的一个实例可以具有以下方法
assemblies
assemblies<<(object, ...)
assemblies.delete(object, ...)
assemblies.destroy(object, ...)
assemblies=(objects)
assembly_ids
assembly_ids=(ids)
assemblies.clear
assemblies.empty?
assemblies.size
assemblies.find(...)
assemblies.where(...)
assemblies.exists?(...)
assemblies.build(attributes = {}, ...)
assemblies.create(attributes = {})
assemblies.create!(attributes = {})
assemblies.reload
2.6.1.1. 管理集合
collection 方法返回所有关联对象的 Relation。如果没有关联对象,它返回一个空的 Relation。
@assemblies = @part.assemblies
collection<< 方法通过在连接表中创建记录来向集合添加一个或多个对象。
@part.assemblies << @assembly1
此方法别名为 collection.concat 和 collection.push。
collection.delete 方法通过删除连接表中的记录来从集合中删除一个或多个对象。这不会销毁对象。
@part.assemblies.delete(@assembly1)
collection.destroy 方法通过删除连接表中的记录来从集合中删除一个或多个对象。这不会销毁对象。
@part.assemblies.destroy(@assembly1)
collection.clear 方法通过删除连接表中的行来从集合中删除所有对象。这不会销毁关联对象。
2.6.1.2. 分配集合
collection= 方法通过适当的添加和删除,使集合仅包含提供的对象。更改将持久化到数据库。
collection_singular_ids= 方法通过适当的添加和删除,使集合仅包含由提供的主键值标识的对象。更改将持久化到数据库。
2.6.1.3. 查询集合
collection_singular_ids 方法返回集合中对象的 id 数组。
@assembly_ids = @part.assembly_ids
collection.empty? 方法返回 true 如果集合不包含任何关联对象。
<% if @part.assemblies.empty? %>
This part is not used in any assemblies
<% end %>
collection.size 方法返回集合中对象的数量。
@assembly_count = @part.assemblies.size
collection.find 方法在集合的表中查找对象。
@assembly = @part.assemblies.find(1)
collection.where 方法根据提供的条件在集合中查找对象,但对象是延迟加载的,这意味着只有在访问对象时才查询数据库。
@new_assemblies = @part.assemblies.where("created_at > ?", 2.days.ago)
collection.exists? 方法检查集合的表中是否存在满足提供条件的对象。
2.6.1.4. 构建和创建关联对象
collection.build 方法返回关联类型的新对象。此对象将从传递的属性实例化,并通过连接表创建链接,但关联对象将尚未保存。
@assembly = @part.assemblies.build({ assembly_name: "Transmission housing" })
collection.create 方法返回关联类型的新对象。此对象将从传递的属性实例化,并通过连接表创建链接,并且,一旦通过关联模型上指定的所有验证,关联对象将被保存。
@assembly = @part.assemblies.create({ assembly_name: "Transmission housing" })
collection.create! 执行与 collection.create 相同操作,但如果记录无效则引发 ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid。
collection.reload 方法返回所有关联对象的 Relation,强制从数据库读取。如果没有关联对象,它返回一个空的 Relation。
@assemblies = @part.assemblies.reload
2.6.1.5. 对象何时保存?
当你将对象分配给 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联时,该对象会自动保存(以便更新连接表)。如果你在一个语句中分配多个对象,那么它们都将被保存。
如果这些保存中的任何一个因验证错误而失败,则赋值语句返回 false,并且赋值本身被取消。
如果父对象(声明 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联的对象)未保存(即 new_record? 返回 true),则子对象在添加时不会保存。关联的所有未保存成员将在父对象保存时自动保存。
如果你想将对象分配给 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联而不保存对象,请使用 collection.build 方法。
3. 选择关联
3.1. belongs_to 与 has_one
如果你想在两个模型之间设置一对一关系,你可以选择 belongs_to 或 has_one 关联。你怎么知道选择哪一个?
区别在于外键的放置位置,外键位于声明 belongs_to 关联的类的表上。然而,了解语义以确定正确的关联至关重要
belongs_to:此关联表示当前模型包含外键并且是关系中的子级。它引用另一个模型,这意味着此模型的每个实例都链接到另一个模型的一个实例。has_one:此关联表示当前模型是关系中的父级,并且它拥有另一个模型的一个实例。
例如,考虑一个涉及供应商及其账户的场景。说一个供应商拥有/拥有一个账户(供应商是父级)比说一个账户拥有/拥有一个供应商更有意义。因此,正确的关联将是
- 一个供应商有一个账户。
- 一个账户属于一个供应商。
以下是你如何在 Rails 中定义这些关联
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account
end
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier
end
要实现这些关联,你需要创建相应的数据库表并设置外键。以下是一个示例迁移
class CreateSuppliers < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :suppliers do |t|
t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
create_table :accounts do |t|
t.belongs_to :supplier_id
t.string :account_number
t.timestamps
end
add_index :accounts, :supplier_id
end
end
请记住,外键位于声明 belongs_to 关联的类的表上。在本例中为 account 表。
3.2. has_many :through 与 has_and_belongs_to_many
Rails 提供了两种不同的方式来声明模型之间的多对多关系:has_many :through 和 has_and_belongs_to_many。了解它们之间的差异和用例可以帮助你为应用程序的需求选择最佳方法。
has_many :through 关联通过中间模型(也称为连接模型)设置多对多关系。这种方法更灵活,允许你向连接模型添加验证、回调和额外属性。连接表需要一个 primary_key(或复合主键)。
class Assembly < ApplicationRecord
has_many :manifests
has_many :parts, through: :manifests
end
class Manifest < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :assembly
belongs_to :part
end
class Part < ApplicationRecord
has_many :manifests
has_many :assemblies, through: :manifests
end
当你需要以下情况时,你会使用 has_many :through
has_and_belongs_to_many 关联允许你直接在两个模型之间创建多对多关系,而无需中间模型。这种方法简单明了,适用于不需要在连接表上额外属性或行为的简单关联。对于 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联,你需要创建一个没有主键的连接表。
class Assembly < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :parts
end
class Part < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies
end
当你需要以下情况时,你会使用 has_and_belongs_to_many
- 关联很简单,不需要在连接表上额外属性或行为。
- 你不需要在连接表上进行验证、回调或额外方法。
4. 高级关联
4.1. 多态关联
关联的一种稍微更高级的变体是多态关联。Rails 中的多态关联允许一个模型通过单个关联属于多个其他模型。当你有一个模型需要链接到不同类型的模型时,这会特别有用。
例如,假设你有一个 Picture 模型,它可以属于 一个 Employee 或 一个 Product,因为每个都可以有一个个人资料图片。这可以这样声明
class Picture < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :imageable, polymorphic: true
end
class Employee < ApplicationRecord
has_many :pictures, as: :imageable
end
class Product < ApplicationRecord
has_many :pictures, as: :imageable
end
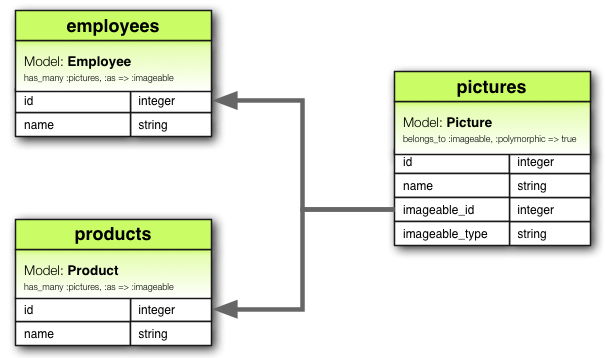
在上述上下文中,imageable 是为关联选择的名称。它是一个符号名称,表示 Picture 模型与 Employee 和 Product 等其他模型之间的多态关联。重要的是在所有关联模型中一致地使用相同的名称 (imageable) 以正确建立多态关联。
当你在 Picture 模型中声明 belongs_to :imageable, polymorphic: true 时,你是在说 Picture 可以通过此关联属于任何模型(例如 Employee 或 Product)。
你可以将多态的 belongs_to 声明视为设置了一个任何其他模型都可以使用的接口。这允许你使用 @employee.pictures 从 Employee 模型实例中检索图片集合。同样,你可以使用 @product.pictures 从 Product 模型实例中检索图片集合。
此外,如果你有一个 Picture 模型的实例,你可以通过 @picture.imageable 获取其父级,这可能是 Employee 或 Product。
要手动设置多态关联,你需要在模型中声明外键列 (imageable_id) 和类型列 (imageable_type)
class CreatePictures < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :pictures do |t|
t.string :name
t.bigint :imageable_id
t.string :imageable_type
t.timestamps
end
add_index :pictures, [:imageable_type, :imageable_id]
end
end
在我们的示例中,imageable_id 可以是 Employee 或 Product 的 ID,而 imageable_type 是关联模型类的名称,因此是 Employee 或 Product。
虽然手动创建多态关联是可接受的,但建议使用 t.references 或其别名 t.belongs_to 并指定 polymorphic: true,以便 Rails 知道该关联是多态的,并且它会自动将外键和类型列添加到表中。
class CreatePictures < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :pictures do |t|
t.string :name
t.belongs_to :imageable, polymorphic: true
t.timestamps
end
end
end
由于多态关联依赖于在数据库中存储类名,因此该数据必须与 Ruby 代码使用的类名保持同步。重命名类时,请务必更新多态类型列中的数据。
例如,如果你将类名从 Product 更改为 Item,则你需要运行迁移脚本以使用新的类名更新 pictures 表(或受影响的任何表)中的 imageable_type 列。此外,你还需要更新应用程序代码中对类名的任何其他引用以反映更改。
4.2. 具有复合主键的模型
Rails 通常可以推断关联模型之间的主键-外键关系,但在处理复合主键时,Rails 通常默认仅使用复合键的一部分,通常是 id 列,除非明确指示。
如果你正在使用 Rails 模型中的复合主键,并且需要确保正确处理关联,请参阅复合主键指南的关联部分。本节提供了在 Rails 中设置和使用具有复合主键的关联的全面指导,包括如何在必要时指定复合外键。
4.3. 自连接
自连接是一种常规连接,但表与自身连接。这在单个表中存在层次关系的情况下很有用。一个常见的例子是员工管理系统,其中员工可以有经理,而该经理也是一名员工。
考虑一个组织,其中员工可以是其他员工的经理。我们希望使用一个 employees 表来跟踪这种关系。
在你的 Rails 模型中,你定义 Employee 类以反映这些关系
class Employee < ApplicationRecord
# an employee can have many subordinates.
has_many :subordinates, class_name: "Employee", foreign_key: "manager_id"
# an employee can have one manager.
belongs_to :manager, class_name: "Employee", optional: true
end
has_many :subordinates 建立一对多关系,其中员工可以有多个下属。在这里,我们指定相关模型也是 Employee (class_name: "Employee"),用于标识经理的外键是 manager_id。
belongs_to :manager 建立一对一关系,其中员工可以属于一个经理。同样,我们将相关模型指定为 Employee。
为了支持这种关系,我们需要向 employees 表添加一个 manager_id 列。此列引用另一个员工(经理)的 id。
class CreateEmployees < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :employees do |t|
# Add a belongs_to reference to the manager, which is an employee.
t.belongs_to :manager, foreign_key: { to_table: :employees }
t.timestamps
end
end
end
t.belongs_to :manager将manager_id列添加到employees表中。foreign_key: { to_table: :employees }确保manager_id列引用employees表的id列。
传递给 foreign_key 的 to_table 选项以及更多内容在SchemaStatements#add_reference中解释。
通过此设置,你可以轻松访问 Rails 应用程序中员工的下属和经理。
获取员工的下属
employee = Employee.find(1)
subordinates = employee.subordinates
获取员工的经理
manager = employee.manager
5. 单表继承 (STI)
单表继承 (STI) 是 Rails 中的一种模式,它允许将多个模型存储在单个数据库表中。当你拥有具有共同属性和行为但也有特定行为的不同类型的实体时,这很有用。
例如,假设我们有 Car、Motorcycle 和 Bicycle 模型。这些模型将共享 color 和 price 等字段,但每个模型都将具有独特的行为。它们还将各自拥有自己的控制器。
5.1. 生成基础 Vehicle 模型
首先,我们生成具有共享字段的基础 Vehicle 模型
$ bin/rails generate model vehicle type:string color:string price:decimal{10.2}
这里,type 字段对于 STI 至关重要,因为它存储模型名称(Car、Motorcycle 或 Bicycle)。STI 需要此字段来区分存储在同一表中的不同模型。
5.2. 生成子模型
接下来,我们生成继承自 Vehicle 的 Car、Motorcycle 和 Bicycle 模型。这些模型将不会有自己的表;相反,它们将使用 vehicles 表。
生成 Car 模型
$ bin/rails generate model car --parent=Vehicle
为此,我们可以使用 --parent=PARENT 选项,它将生成一个继承自指定父级且没有相应迁移的模型(因为表已经存在)。
这会生成一个继承自 Vehicle 的 Car 模型
class Car < Vehicle
end
这意味着添加到 Vehicle 的所有行为都可用于 Car,例如关联、公共方法等。创建汽车将把它保存在 vehicles 表中,type 字段为“Car”
对 Motorcycle 和 Bicycle 重复相同的过程。
5.3. 创建记录
创建 Car 的记录
Car.create(color: "Red", price: 10000)
这将生成以下 SQL
INSERT INTO "vehicles" ("type", "color", "price") VALUES ('Car', 'Red', 10000)
5.4. 查询记录
查询汽车记录将只搜索作为汽车的车辆
Car.all
将运行类似这样的查询
SELECT "vehicles".* FROM "vehicles" WHERE "vehicles"."type" IN ('Car')
5.5. 添加特定行为
你可以向子模型添加特定行为或方法。例如,向 Car 模型添加一个方法
class Car < Vehicle
def honk
"Beep Beep"
end
end
现在你可以在 Car 实例上调用 honk 方法
car = Car.first
car.honk
# => 'Beep Beep'
5.6. 控制器
每个模型都可以有自己的控制器。例如,CarsController
# app/controllers/cars_controller.rb
class CarsController < ApplicationController
def index
@cars = Car.all
end
end
5.7. 覆盖继承列
有时(例如在使用遗留数据库时),你可能需要覆盖继承列的名称。这可以通过inheritance_column 方法实现。
# Schema: vehicles[ id, kind, created_at, updated_at ]
class Vehicle < ApplicationRecord
self.inheritance_column = "kind"
end
class Car < Vehicle
end
Car.create(color: "Red", price: 10000)
# => #<Car kind: "Car", color: "Red", price: 10000>
在此设置中,Rails 将使用 kind 列存储模型类型,允许 STI 使用自定义列名正常运行。
5.8. 禁用继承列
有时(例如在使用遗留数据库时),你可能需要完全禁用单表继承。如果你没有正确禁用 STI,你可能会遇到ActiveRecord::SubclassNotFound 错误。
要禁用 STI,你可以将inheritance_column 设置为 nil。
# Schema: vehicles[ id, type, created_at, updated_at ]
class Vehicle < ApplicationRecord
self.inheritance_column = nil
end
Vehicle.create!(type: "Car", color: "Red", price: 10000)
# => #<Vehicle type: "Car", color: "Red", price: 10000>
在此配置中,Rails 将把类型列视为普通属性,并且不会将其用于 STI 目的。如果你需要处理不遵循 STI 模式的遗留模式,这会很有用。
这些调整在将 Rails 与现有数据库集成或需要对模型进行特定自定义时提供了灵活性。
5.9. 注意事项
单表继承 (STI) 在子类及其属性之间差异不大时效果最佳,但它将所有子类的所有属性都包含在一个表中。
这种方法的缺点是它可能导致表膨胀,因为该表将包含每个子类特有的属性,即使它们不被其他子类使用。这可以通过使用委托类型来解决。
此外,如果你正在使用多态关联,其中一个模型可以通过类型和 ID 属于多个其他模型,那么维护参照完整性可能会变得复杂,因为关联逻辑必须正确处理不同的类型。
最后,如果你的子类之间存在特定的数据完整性检查或验证,你需要确保 Rails 或数据库正确处理这些问题,尤其是在设置外键约束时。
6. 委托类型
委托类型通过 delegated_type 解决了单表继承 (STI) 表膨胀的问题。这种方法允许我们将共享属性存储在超类表中,并为子类特定的附加属性使用单独的表。
6.1. 设置委托类型
要使用委托类型,我们需要按如下方式建模数据
- 有一个超类,它将所有子类之间的共享属性存储在其表中。
- 每个子类都必须继承自超类,并且将有一个单独的表用于其特定的任何附加属性。
这消除了在单个表中定义所有子类之间无意共享的属性的需要。
6.2. 生成模型
为了将其应用于我们上面的示例,我们需要重新生成我们的模型。
首先,让我们生成将作为我们超类的基础 Entry 模型
$ bin/rails generate model entry entryable_type:string entryable_id:integer
然后,我们将为委托生成新的 Message 和 Comment 模型
$ bin/rails generate model message subject:string body:string
$ bin/rails generate model comment content:string
如果你没有为字段指定类型(例如,subject 而不是 subject:string),Rails 将默认为 string 类型。
运行生成器后,我们的模型应如下所示
# Schema: entries[ id, entryable_type, entryable_id, created_at, updated_at ]
class Entry < ApplicationRecord
end
# Schema: messages[ id, subject, body, created_at, updated_at ]
class Message < ApplicationRecord
end
# Schema: comments[ id, content, created_at, updated_at ]
class Comment < ApplicationRecord
end
6.3. 声明 delegated_type
首先,在超类 Entry 中声明一个 delegated_type。
class Entry < ApplicationRecord
delegated_type :entryable, types: %w[ Message Comment ], dependent: :destroy
end
entryable 参数指定用于委托的字段,并包含 Message 和 Comment 作为委托类。entryable_type 和 entryable_id 字段分别存储子类名称和委托子类的记录 ID。
6.4. 定义 Entryable 模块
接下来,通过在 has_one 关联中声明 as: :entryable 参数来定义一个模块以实现这些委托类型。
module Entryable
extend ActiveSupport::Concern
included do
has_one :entry, as: :entryable, touch: true
end
end
在你的子类中包含创建的模块
class Message < ApplicationRecord
include Entryable
end
class Comment < ApplicationRecord
include Entryable
end
完成此定义后,我们的 Entry 委托器现在提供以下方法
| 方法 | 返回 |
|---|---|
Entry.entryable_types |
["Message", "Comment"] |
Entry#entryable_class |
Message 或 Comment |
Entry#entryable_name |
"message" 或 "comment" |
Entry.messages |
Entry.where(entryable_type: "Message") |
Entry#message? |
当 entryable_type == "Message" 时返回 true |
Entry#message |
当 entryable_type == "Message" 时返回消息记录,否则返回 nil |
Entry#message_id |
当 entryable_type == "Message" 时返回 entryable_id,否则返回 nil |
Entry.comments |
Entry.where(entryable_type: "Comment") |
Entry#comment? |
当 entryable_type == "Comment" 时返回 true |
Entry#comment |
当 entryable_type == "Comment" 时返回评论记录,否则返回 nil |
Entry#comment_id |
当 entryable_type == "Comment" 时返回 entryable_id,否则返回 nil |
6.5. 对象创建
创建新的 Entry 对象时,我们可以同时指定 entryable 子类。
Entry.create! entryable: Message.new(subject: "hello!")
6.6. 添加进一步委托
我们可以通过定义 delegate 并在子类上使用多态性来增强我们的 Entry 委托器。例如,将 title 方法从 Entry 委托给其子类
class Entry < ApplicationRecord
delegated_type :entryable, types: %w[ Message Comment ]
delegate :title, to: :entryable
end
class Message < ApplicationRecord
include Entryable
def title
subject
end
end
class Comment < ApplicationRecord
include Entryable
def title
content.truncate(20)
end
end
此设置允许 Entry 将 title 方法委托给其子类,其中 Message 使用 subject,Comment 使用 content 的截断版本。
7. 提示、技巧和警告
以下是你在 Rails 应用程序中有效使用 Active Record 关联需要了解的一些事项
- 控制缓存
- 避免名称冲突
- 更新 Schema
- 控制关联作用域
- 双向关联
7.1. 控制关联缓存
所有关联方法都围绕缓存构建,它保留已加载关联的结果以供进一步操作。缓存甚至在方法之间共享。例如
# retrieves books from the database
author.books.load
# uses the cached copy of books
author.books.size
# uses the cached copy of books
author.books.empty?
当我们使用 author.books 时,数据不会立即从数据库加载。相反,它会设置一个查询,该查询将在你实际尝试使用数据时执行,例如,通过调用需要数据的方法,如 each、size、empty? 等。通过在调用使用数据的其他方法之前调用 author.books.load,你明确触发查询以立即从数据库加载数据。如果你知道你需要数据并希望避免在处理关联时触发多个查询可能带来的性能开销,这会很有用。
但如果你想重新加载缓存怎么办,因为数据可能已被应用程序的其他部分更改?只需在关联上调用reload
# retrieves books from the database
author.books.load
# uses the cached copy of books
author.books.size
# discards the cached copy of books and goes back to the database
author.books.reload.empty?
7.2. 避免名称冲突
在 Ruby on Rails 模型中创建关联时,避免使用已用于 ActiveRecord::Base 实例方法的名称非常重要。这是因为创建与现有方法冲突的名称的关联可能会导致意外后果,例如覆盖基本方法并导致功能问题。例如,将 attributes 或 connection 等名称用于关联将是有问题的。
7.3. 更新 Schema
关联非常有用,它们负责定义模型之间的关系,但它们不会更新你的数据库 Schema。你需要负责维护你的数据库 Schema 以匹配你的关联。这通常涉及两个主要任务:为belongs_to 关联创建外键,以及为has_many :through 和has_and_belongs_to_many 关联设置正确的连接表。你可以在has many through vs has and belongs to many 部分阅读有关何时使用 has_many :through vs has_and_belongs_to_many 的更多信息。
7.3.1. 为 belongs_to 关联创建外键
当你声明belongs_to 关联时,你需要酌情创建外键。例如,考虑此模型
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author
end
此声明需要由 books 表中相应的 FOREIGN KEY 列支持。对于一个全新的表,迁移可能看起来像这样
class CreateBooks < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :books do |t|
t.datetime :published_at
t.string :book_number
t.belongs_to :author
end
end
end
而对于现有表,它可能看起来像这样
class AddAuthorToBooks < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
add_reference :books, :author
end
end
7.3.2. 为 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联创建连接表
如果你创建 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联,你需要明确创建连接表。除非使用 :join_table 选项明确指定连接表的名称,否则 Active Record 将使用类名的词法顺序创建名称。因此,作者和书籍模型之间的连接将给出默认连接表名称“authors_books”,因为“a”在词法排序中领先于“b”。
无论名称是什么,你都必须使用适当的迁移手动生成连接表。例如,考虑这些关联
class Assembly < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :parts
end
class Part < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies
end
这些需要由创建 assemblies_parts 表的迁移支持。
$ bin/rails generate migration CreateAssembliesPartsJoinTable assemblies parts
然后你可以填写迁移并确保在没有主键的情况下创建表。
class CreateAssembliesPartsJoinTable < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :assemblies_parts, id: false do |t|
t.bigint :assembly_id
t.bigint :part_id
end
add_index :assemblies_parts, :assembly_id
add_index :assemblies_parts, :part_id
end
end
我们向 create_table 传递 id: false,因为连接表不代表模型。如果你在 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联中发现任何奇怪的行为,例如模型 ID 损坏,或关于 ID 冲突的异常,那么你很可能忘记在创建迁移时设置 id: false。
为简单起见,你也可以使用 create_join_table 方法
class CreateAssembliesPartsJoinTable < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_join_table :assemblies, :parts do |t|
t.index :assembly_id
t.index :part_id
end
end
end
你可以在Active Record 迁移指南中阅读有关 create_join_table 方法的更多信息
7.3.3. 为 has_many :through 关联创建连接表
为 has_many :through 与 has_and_belongs_to_many 创建连接表之间的 Schema 实现主要区别在于 has_many :through 的连接表需要一个 id。
class CreateAppointments < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
create_table :appointments do |t|
t.belongs_to :physician
t.belongs_to :patient
t.datetime :appointment_date
t.timestamps
end
end
end
7.4. 控制关联作用域
默认情况下,关联只在当前模块的作用域内查找对象。此功能在模块内声明 Active Record 模型时特别有用,因为它使关联正确作用域。例如
module MyApplication
module Business
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account
end
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier
end
end
end
在此示例中,Supplier 和 Account 类都在同一模块 (MyApplication::Business) 中定义。此组织允许你根据其作用域将模型结构化到文件夹中,而无需在每个关联中显式指定作用域
# app/models/my_application/business/supplier.rb
module MyApplication
module Business
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account
end
end
end
# app/models/my_application/business/account.rb
module MyApplication
module Business
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier
end
end
end
需要注意的是,虽然模型作用域有助于组织代码,但它不会更改数据库表的命名约定。例如,如果你有一个 MyApplication::Business::Supplier 模型,相应的数据库表仍应遵循命名约定并命名为 my_application_business_suppliers。
但是,如果 Supplier 和 Account 模型在不同的作用域中定义,则关联默认情况下将无法工作
module MyApplication
module Business
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account
end
end
module Billing
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier
end
end
end
要将模型与不同命名空间中的模型关联,你必须在关联声明中指定完整的类名
module MyApplication
module Business
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account,
class_name: "MyApplication::Billing::Account"
end
end
module Billing
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier,
class_name: "MyApplication::Business::Supplier"
end
end
end
通过显式声明 class_name 选项,你可以跨不同的命名空间创建关联,确保无论其模块作用域如何,都能正确链接模型。
7.5. 双向关联
在 Rails 中,模型之间的关联通常是双向的,这意味着它们需要在两个相关模型中声明。请考虑以下示例
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
end
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author
end
Active Record 将尝试根据关联名称自动识别这两个模型共享双向关联。此信息允许 Active Record
避免对已加载数据进行不必要的查询
Active Record 避免对已加载数据进行额外的数据库查询。
irb> author = Author.first irb> author.books.all? do |book| irb> book.author.equal?(author) # No additional queries executed here irb> end => true防止数据不一致
由于只加载了一个
Author对象的副本,这有助于防止不一致。irb> author = Author.first irb> book = author.books.first irb> author.name == book.author.name => true irb> author.name = "Changed Name" irb> author.name == book.author.name => true在更多情况下自动保存关联
irb> author = Author.new irb> book = author.books.new irb> book.save! irb> book.persisted? => true irb> author.persisted? => trueirb> book = Book.new irb> book.valid? => false irb> book.errors.full_messages => ["Author must exist"] irb> author = Author.new irb> book = author.books.new irb> book.valid? => true
有时,你可能需要使用 :foreign_key 或 :class_name 等选项自定义关联。当你这样做时,Rails 可能无法自动识别涉及 :through 或 :foreign_key 选项的双向关联。
相反关联上的自定义作用域也阻止自动识别,除非将config.active_record.automatic_scope_inversing 设置为 true,否则关联本身上的自定义作用域也会阻止自动识别。
例如,考虑以下具有自定义外键的模型声明
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
end
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :writer, class_name: "Author", foreign_key: "author_id"
end
由于 :foreign_key 选项,Active Record 将不会自动识别双向关联,这可能导致以下几个问题
对相同数据执行不必要的查询(在此示例中导致 N+1 查询)
irb> author = Author.first irb> author.books.any? do |book| irb> book.writer.equal?(author) # This executes an author query for every book irb> end => false引用具有不一致数据的模型多个副本
irb> author = Author.first irb> book = author.books.first irb> author.name == book.writer.name => true irb> author.name = "Changed Name" irb> author.name == book.writer.name => false无法自动保存关联
irb> author = Author.new irb> book = author.books.new irb> book.save! irb> book.persisted? => true irb> author.persisted? => false无法验证存在性或不存在性
irb> author = Author.new irb> book = author.books.new irb> book.valid? => false irb> book.errors.full_messages => ["Author must exist"]
要解决这些问题,你可以使用 :inverse_of 选项显式声明双向关联
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, inverse_of: "writer"
end
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :writer, class_name: "Author", foreign_key: "author_id"
end
通过在 has_many 关联声明中包含 :inverse_of 选项,Active Record 将识别双向关联并按照上述初始示例中的行为行事。
8. 关联引用
8.1. 选项
虽然 Rails 使用智能默认值在大多数情况下都能很好地工作,但有时你可能希望自定义关联引用的行为。此类自定义可以通过在创建关联时传递选项块来完成。例如,此关联使用两个此类选项
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, touch: :books_updated_at,
counter_cache: true
end
每个关联都支持众多选项,你可以在ActiveRecord 关联 API 中每个关联的 Options 部分阅读更多信息。我们将在下面讨论一些常见的用例。
8.1.1. :class_name
如果无法从关联名称派生另一个模型的名称,则可以使用 :class_name 选项提供模型名称。例如,如果一本书属于一位作者,但包含作者的模型的实际名称是 Patron,则你将这样设置
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, class_name: "Patron"
end
此选项在多态关联中不受支持,因为在这种情况下,关联记录的类名存储在类型列中。
8.1.2. :dependent
控制关联对象在其所有者被销毁时会发生什么
:destroy,当对象被销毁时,将对其关联对象调用destroy。此方法不仅从数据库中删除关联记录,还确保执行任何定义的回调(例如before_destroy和after_destroy)。这对于在删除过程中执行自定义逻辑很有用,例如日志记录或清理相关数据。:delete,当对象被销毁时,其所有关联对象将直接从数据库中删除,而不会调用其destroy方法。此方法执行直接删除并绕过关联模型中的任何回调或验证,使其更高效,但如果跳过重要的清理任务,则可能导致数据完整性问题。当你需要快速删除记录并确信关联记录不需要额外操作时,请使用delete。:destroy_async:当对象被销毁时,会排队一个ActiveRecord::DestroyAssociationAsyncJob作业,该作业将对其关联对象调用 destroy。必须设置 Active Job 才能使其工作。如果关联在数据库中由外键约束支持,请勿使用此选项。外键约束操作将在删除其所有者的同一事务中发生。:nullify导致外键设置为NULL。多态关联上的多态类型列也会被 nullified。不执行回调。:restrict_with_exception导致在存在关联记录时引发ActiveRecord::DeleteRestrictionError异常:restrict_with_error导致在存在关联对象时向所有者添加错误
你不应在与另一个类上的 has_many 关联连接的 belongs_to 关联上指定此选项。这样做可能导致数据库中出现孤立记录,因为销毁父对象可能会尝试销毁其子对象,这反过来又可能再次尝试销毁父对象,从而导致不一致。
不要为具有 NOT NULL 数据库约束的关联保留 :nullify 选项。将 dependent 设置为 :destroy 至关重要;否则,关联对象的外键可能会设置为 NULL,从而阻止对其进行更改。
:dependent 选项在与 :through 选项一起使用时被忽略。使用 :through 时,连接模型必须具有 belongs_to 关联,并且删除仅影响连接记录,而不影响关联记录。
在作用域关联上使用 dependent: :destroy 时,只会销毁作用域对象。例如,在定义为 has_many :comments, -> { where published: true }, dependent: :destroy 的 Post 模型中,调用销毁文章将只删除已发布的评论,未发布的评论将保留其外键指向已删除的文章。
你不能直接在 has_and_belongs_to_many 关联上使用 :dependent 选项。要管理连接表记录的删除,请手动处理它们或切换到 has_many :through 关联,它提供更大的灵活性并支持 :dependent 选项。
8.1.3. :foreign_key
按照约定,Rails 假定此模型上用于保存外键的列是带有 _id 后缀的关联名称。:foreign_key 选项允许你直接设置外键的名称
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account, foreign_key: "supp_id"
end
Rails 不会为你创建外键列。你需要在迁移中明确定义它们。
8.1.4. :primary_key
默认情况下,Rails 使用 id 列作为其表的主键。:primary_key 选项允许您指定不同的列作为主键。
例如,如果 users 表使用 guid 作为主键而不是 id,并且您希望 todos 表将 guid 作为外键 (user_id) 引用,您可以这样配置
class User < ApplicationRecord
self.primary_key = "guid" # Sets the primary key to guid instead of id
end
class Todo < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :user, primary_key: "guid" # References the guid column in users table
end
当您执行 @user.todos.create 时,@todo 记录的 user_id 值将被设置为 @user 的 guid 值。
has_and_belongs_to_many 不支持 :primary_key 选项。对于这种类型的关联,您可以通过使用带有 has_many :through 关联的连接表来实现类似的功能,这提供了更大的灵活性并支持 :primary_key 选项。您可以在 has_many :through 章节中阅读更多相关信息。
8.1.5. :touch
如果您将 :touch 选项设置为 true,那么每当此对象被保存或销毁时,关联对象的 updated_at 或 updated_on 时间戳将被设置为当前时间
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, touch: true
end
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
end
在这种情况下,保存或销毁一本书将更新关联作者的时间戳。您还可以指定要更新的特定时间戳属性
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, touch: :books_updated_at
end
has_and_belongs_to_many 不支持 :touch 选项。对于这种类型的关联,您可以通过使用带有 has_many :through 关联的连接表来实现类似的功能。您可以在 has_many :through 章节中阅读更多相关信息。
8.1.6. :validate
如果您将 :validate 选项设置为 true,那么每当您保存此对象时,新的关联对象都将被验证。默认情况下,这是 false:当此对象保存时,新的关联对象将不会被验证。
has_and_belongs_to_many 不支持 :validate 选项。对于这种类型的关联,您可以通过使用带有 has_many :through 关联的连接表来实现类似的功能。您可以在 has_many :through 章节中阅读更多相关信息。
8.1.7. :inverse_of
:inverse_of 选项指定此关联的逆关联 belongs_to 关联的名称。有关更多详细信息,请参阅双向关联章节。
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account, inverse_of: :supplier
end
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier, inverse_of: :account
end
8.1.8. :source_type
:source_type 选项指定通过多态关联进行的 has_many :through 关联的源关联类型。
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
has_many :paperbacks, through: :books, source: :format, source_type: "Paperback"
end
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :format, polymorphic: true
end
class Hardback < ApplicationRecord; end
class Paperback < ApplicationRecord; end
8.1.9. :strict_loading
每次通过此关联加载关联记录时,强制执行严格加载。
8.1.10. :association_foreign_key
:association_foreign_key 可以在 has_and_belongs_to_many 关系中找到。根据约定,Rails 假定连接表中用于保存指向其他模型的外键的列是该模型的名称加上 _id 后缀。:association_foreign_key 选项允许您直接设置外键的名称。例如
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :friends,
class_name: "User",
foreign_key: "this_user_id",
association_foreign_key: "other_user_id"
end
:foreign_key 和 :association_foreign_key 选项在设置多对多自连接时很有用。
8.1.11. :join_table
:join_table 可以在 has_and_belongs_to_many 关系中找到。如果基于词典顺序的连接表的默认名称不是您想要的,您可以使用 :join_table 选项覆盖默认值。
8.1.12. :deprecated
如果为 true,Active Record 会在每次使用关联时发出警告。
支持三种报告模式(:warn、:raise 和 :notify),并且可以启用或禁用回溯。默认值为 :warn 模式和禁用回溯。
请查看 ActiveRecord::Associations::ClassMethods 的文档以获取更多详细信息。
8.2. 作用域
作用域允许您指定可以作为关联对象上的方法调用引用的常见查询。这对于定义在应用程序中多个地方重用的自定义查询很有用。例如
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies, -> { where active: true }
end
8.2.1. 一般作用域
您可以在作用域块内使用任何标准查询方法。下面讨论以下方法
whereincludesreadonlyselect
8.2.1.1. where
where 方法允许您指定关联对象必须满足的条件。
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies,
-> { where "factory = 'Seattle'" }
end
您还可以通过哈希设置条件
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies,
-> { where factory: "Seattle" }
end
如果您使用哈希样式的 where,那么通过此关联创建记录将自动使用哈希进行作用域。在这种情况下,使用 @parts.assemblies.create 或 @parts.assemblies.build 将创建 factory 列值为“Seattle”的程序集。
8.2.1.2. includes
您可以使用 includes 方法指定在使用此关联时应预加载的二阶关联。例如,考虑这些模型
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account
end
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier
belongs_to :representative
end
class Representative < ApplicationRecord
has_many :accounts
end
如果您经常直接从供应商检索代表(@supplier.account.representative),那么通过在从供应商到账户的关联中包含代表,可以使您的代码效率更高一些
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account, -> { includes :representative }
end
class Account < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :supplier
belongs_to :representative
end
class Representative < ApplicationRecord
has_many :accounts
end
不需要对即时关联使用 includes——也就是说,如果您有 Book belongs_to :author,那么作者在需要时会自动预加载。
8.2.1.3. readonly
如果您使用 readonly,那么通过关联检索到的关联对象将是只读的。
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, -> { readonly }
end
当您想要防止通过关联修改关联对象时,这很有用。例如,如果您有一个 Book 模型,它 belongs_to :author,您可以使用 readonly 来防止通过图书修改作者
@book.author = Author.first
@book.author.save! # This will raise an ActiveRecord::ReadOnlyRecord error
8.2.1.4. select
select 方法允许您覆盖用于检索关联对象数据的 SQL SELECT 子句。默认情况下,Rails 检索所有列。
例如,如果您有一个包含许多 Book 的 Author 模型,但您只希望检索每本书的 title
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, -> { select(:id, :title) } # Only select id and title columns
end
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author
end
现在,当您访问作者的书籍时,将只从 books 表中检索 id 和 title 列。
如果您在 belongs_to 关联上使用 select 方法,您还应该设置 :foreign_key 选项以保证正确的结果。例如
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, -> { select(:id, :name) }, foreign_key: "author_id" # Only select id and name columns
end
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
end
在这种情况下,当您访问一本书的作者时,将只从 authors 表中检索 id 和 name 列。
8.2.2. 集合作用域
has_many 和 has_and_belongs_to_many 是处理记录集合的关联,因此您可以使用 group、limit、order、select 和 distinct 等附加方法来自定义关联使用的查询。
8.2.2.1. group
group 方法提供一个属性名称,用于在查找器 SQL 中使用 GROUP BY 子句对结果集进行分组。
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies, -> { group "factory" }
end
8.2.2.2. limit
limit 方法允许您限制通过关联获取的对象总数。
class Parts < ApplicationRecord
has_and_belongs_to_many :assemblies,
-> { order("created_at DESC").limit(50) }
end
8.2.2.3. order
order 方法规定了关联对象接收的顺序(使用 SQL ORDER BY 子句的语法)。
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, -> { order "date_confirmed DESC" }
end
8.2.2.4. select
select 方法允许您覆盖用于检索关联对象数据的 SQL SELECT 子句。默认情况下,Rails 检索所有列。
如果您指定自己的 select,请务必包含关联模型的主键和外键列。否则,Rails 将抛出错误。
8.2.2.5. distinct
使用 distinct 方法使集合没有重复项。这主要与 :through 选项一起使用时有用。
class Person < ApplicationRecord
has_many :readings
has_many :articles, through: :readings
end
irb> person = Person.create(name: 'John')
irb> article = Article.create(name: 'a1')
irb> person.articles << article
irb> person.articles << article
irb> person.articles.to_a
=> [#<Article id: 5, name: "a1">, #<Article id: 5, name: "a1">]
irb> Reading.all.to_a
=> [#<Reading id: 12, person_id: 5, article_id: 5>, #<Reading id: 13, person_id: 5, article_id: 5>]
在上述情况下,有两个读数,person.articles 会显示这两个读数,即使这些记录指向同一篇文章。
现在我们设置 distinct
class Person
has_many :readings
has_many :articles, -> { distinct }, through: :readings
end
irb> person = Person.create(name: 'Honda')
irb> article = Article.create(name: 'a1')
irb> person.articles << article
irb> person.articles << article
irb> person.articles.to_a
=> [#<Article id: 7, name: "a1">]
irb> Reading.all.to_a
=> [#<Reading id: 16, person_id: 7, article_id: 7>, #<Reading id: 17, person_id: 7, article_id: 7>]
在上述情况下,仍然有两个读数。但是 person.articles 只显示一篇文章,因为集合只加载唯一的记录。
如果您想确保,在插入时,持久化关联中的所有记录都是唯一的(这样您就可以确保在检查关联时永远不会找到重复记录),您应该在表本身上添加一个唯一索引。例如,如果您有一个名为 readings 的表,并且您想确保文章只能添加到一个人一次,您可以在迁移中添加以下内容
add_index :readings, [:person_id, :article_id], unique: true
一旦您有了这个唯一索引,尝试将文章添加到一个人两次将引发 ActiveRecord::RecordNotUnique 错误
irb> person = Person.create(name: 'Honda')
irb> article = Article.create(name: 'a1')
irb> person.articles << article
irb> person.articles << article
ActiveRecord::RecordNotUnique
请注意,使用 include? 之类的方法检查唯一性会受到竞争条件的影响。不要尝试使用 include? 来强制关联中的唯一性。例如,使用上面文章的例子,以下代码将存在竞争条件,因为多个用户可能同时尝试执行此操作
person.articles << article unless person.articles.include?(article)
8.2.3. 使用关联所有者
您可以将关联的所有者作为单个参数传递给作用域块,以对关联作用域进行更多控制。但是,请注意,这样做将使预加载关联变得不可能。
例如
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_one :account, ->(supplier) { where active: supplier.active? }
end
在此示例中,Supplier 模型的 account 关联根据供应商的 active 状态进行作用域。
通过利用关联扩展和与关联所有者一起进行作用域,您可以在 Rails 应用程序中创建更具动态性和上下文感知的关联。
8.3. 计数缓存
Rails 中的 :counter_cache 选项有助于提高查找关联对象数量的效率。考虑以下模型
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author
end
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
end
默认情况下,查询 author.books.size 会导致数据库调用执行 COUNT(*) 查询。为了优化这一点,您可以在所属模型(在本例中为 Book)中添加计数缓存。这样,Rails 可以直接从缓存返回计数,而无需查询数据库。
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, counter_cache: true
end
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
end
通过此声明,Rails 将使缓存值保持最新,然后将该值作为 size 方法的响应返回,从而避免数据库调用。
尽管 :counter_cache 选项是在带有 belongs_to 声明的模型上指定的,但实际列必须添加到关联模型(在本例中为 has_many)。在此示例中,您需要向 Author 模型添加一个 books_count 列
class AddBooksCountToAuthors < ActiveRecord::Migration[8.1]
def change
add_column :authors, :books_count, :integer, default: 0, null: false
end
end
您可以在 counter_cache 声明中指定自定义列名,而不是使用默认的 books_count。例如,要使用 count_of_books
class Book < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :author, counter_cache: :count_of_books
end
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books
end
您只需在关联的 belongs_to 端指定 :counter_cache 选项。
在现有大型表上使用计数缓存可能会很麻烦。为了避免长时间锁定表,列值必须与列添加分开回填。此回填还必须在使用 :counter_cache 之前发生;否则,依赖计数缓存的方法(例如 size、any? 等)可能会返回不正确的结果。
为了在安全回填值的同时使计数缓存列与子记录创建/删除保持同步,并确保方法始终从数据库获取结果(避免可能不正确的计数缓存值),请使用 counter_cache: { active: false }。此设置确保方法始终从数据库获取结果,从而避免未初始化计数缓存中的不正确值。如果您需要指定自定义列名,请使用 counter_cache: { active: false, column: :my_custom_counter }。
如果由于某种原因您更改了拥有模型主键的值,并且没有同时更新计数模型的外键,那么计数缓存可能包含陈旧数据。换句话说,任何孤立模型仍将计入计数器。要修复陈旧的计数缓存,请使用 reset_counters。
8.4. 回调
普通回调挂钩到 Active Record 对象的生命周期中,允许您在不同时间点处理这些对象。例如,您可以使用 :before_save 回调在保存对象之前执行某些操作。
关联回调类似于普通回调,但它们由与 Active Record 对象关联的集合生命周期中的事件触发。有四种可用的关联回调
before_addafter_addbefore_removeafter_remove
您可以通过向关联声明添加选项来定义关联回调。例如
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, before_add: :check_credit_limit
def check_credit_limit(book)
throw(:abort) if limit_reached?
end
end
在此示例中,Author 模型与 books 具有 has_many 关联。before_add 回调 check_credit_limit 在将图书添加到集合之前触发。如果 limit_reached? 方法返回 true,则该图书不会添加到集合中。
通过使用这些关联回调,您可以自定义关联的行为,确保在集合生命周期的关键点执行特定操作。
在 Active Record 回调指南中阅读有关关联回调的更多信息
8.5. 扩展
Rails 提供了通过匿名模块添加新的查找器、创建器或其他方法来扩展关联代理对象(管理关联)功能的能力。此功能允许您自定义关联以满足应用程序的特定需求。
您可以直接在模型定义中通过自定义方法扩展 has_many 关联。例如
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books do
def find_by_book_prefix(book_number)
find_by(category_id: book_number[0..2])
end
end
end
在此示例中,find_by_book_prefix 方法已添加到 Author 模型的 books 关联中。此自定义方法允许您根据 book_number 的特定前缀查找 books。
如果您有一个应该由多个关联共享的扩展,您可以使用命名扩展模块。例如
module FindRecentExtension
def find_recent
where("created_at > ?", 5.days.ago)
end
end
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, -> { extending FindRecentExtension }
end
class Supplier < ApplicationRecord
has_many :deliveries, -> { extending FindRecentExtension }
end
在这种情况下,FindRecentExtension 模块用于向 Author 模型中的 books 关联和 Supplier 模型中的 deliveries 关联添加 find_recent 方法。此方法检索最近五天内创建的记录。
扩展可以使用 proxy_association 访问器与关联代理的内部进行交互。proxy_association 提供三个重要的属性
proxy_association.owner返回关联所属的对象。proxy_association.reflection返回描述关联的反射对象。proxy_association.target返回belongs_to或has_one的关联对象,或has_many或has_and_belongs_to_many的关联对象集合。
这些属性允许扩展访问和操作关联代理的内部状态和行为。
这是一个高级示例,演示如何在扩展中使用这些属性
module AdvancedExtension
def find_and_log(query)
results = where(query)
proxy_association.owner.logger.info("Querying #{proxy_association.reflection.name} with #{query}")
results
end
end
class Author < ApplicationRecord
has_many :books, -> { extending AdvancedExtension }
end
在此示例中,find_and_log 方法对关联执行查询,并使用所有者的记录器记录查询详细信息。该方法通过 proxy_association.owner 访问所有者的记录器,并通过 proxy_association.reflection.name 访问关联的名称。